The plastic molding process involves using different technologies and machines to transform plastic materials into products with the required shape. During the plastic molding process, changes in physical and chemical properties often occur. There are several ways to shape plastics to certain geometry—you can find their advantages, disadvantages, and best uses here.
Injection Molding
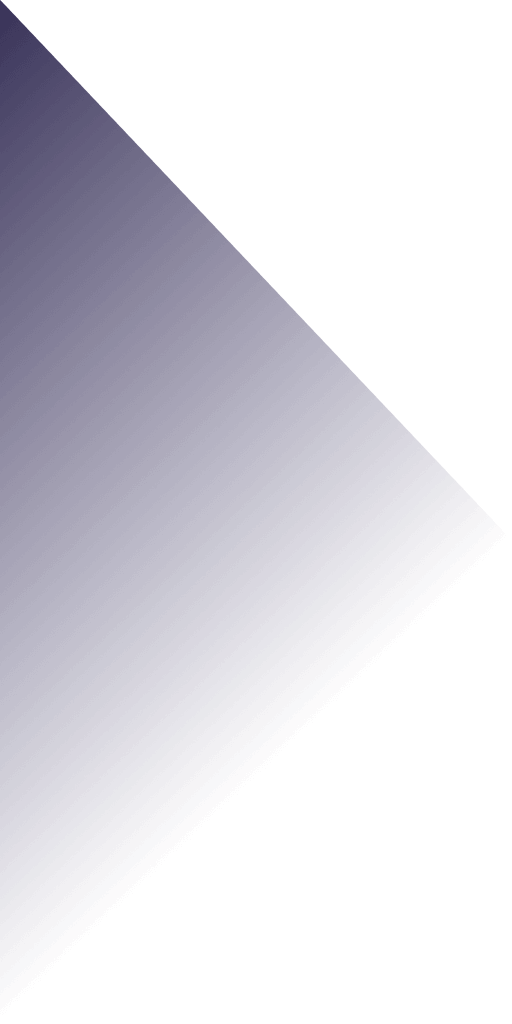
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting material into a mold. The material is forced into the mold cavity and allowed to cool, resulting in a solid product shaped by the mold. The material can be liquid, or it can be melted and injected into the mold.
Injection molding uses heated plastic materials to make them pliable enough to flow through an extruder and into the molding cavity. The plastics then cool and harden, forming a finished plastic part. Injection molded parts are used in almost every industry and application, from automotive and consumer goods to medical devices and electronic components.

Compression Molding
In the compression molding process, heated and softened plastic material is forced into a mold cavity by a plunger or ram. The ram applies pressure to the heated material until it solidifies. When the ram is withdrawn, a solid part remains in the shape of the cavity.
Compression molding is used for high-volume production because it’s efficient, cost-effective, and produces good quality parts. It also allows for lower labor costs than other processes.
The main advantage of compression molding is that it allows one to make a wide variety of products with different shapes and sizes. This process also allows for more intricate designs than other processes such as injection molding because it doesn’t require tooling as dies do.

Extrusion Molding
The plastic molding process is a manufacturing process for producing parts from plastics. The most common plastic materials used in plastic molding are acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), high impact polystyrene (HIPS), and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Other materials include acrylic, nylon, polycarbonate, and even PVC.
Plastic Molding is an accessible way to produce custom parts for any application. Many different types of plastics can be molded into almost any shape. It is also possible to create plastic molds for casting metal parts.
The extrusion molding process involves placing molten plastic inside a heated barrel, which is forced through a shaped die. This process has been used since the mid-1800s when Charles Goodyear developed it as an industrial manufacturing method by which rubber could be forced through dies that would give it its desired shape. The extrusion process was later adapted to plastic production in the 1940s when Ford Motors began using it on their automobiles and other consumer products such as toothbrushes, eyeglasses frames, etc…

Blow Molding
Plastic blow molding is a manufacturing process in which plastic is heated and formed over a hollow metal mold cavity. The heated plastic flows into the mold cavity, where it cools and hardens. At this stage, the two halves of the mold are separated, and the finished product is ejected. The most common uses for blow molded plastics include packaging for food products and containers for liquids, such as detergent bottles.
The main advantage of blow molding is that it can produce large volumes of identical parts at high speeds. In addition, it produces parts with excellent surface finishes and complex shapes that cannot be made by other processes alone.

Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding is one of the most versatile and cost-effective manufacturing processes available. It’s also referred to as roto-molding, roto casting, rotational Molding, and rotational Molding.
The process begins with a mold that can be made from steel or aluminum. The inside of the mold is lined with a release agent to help remove the finished product from the mold. A mixture of plastic resin and colorant is heated in a separate tank until it reaches the proper temperature (typically 195-210 degrees Fahrenheit). The molten material is then injected into the mold under pressure, where it cools and hardens into its final shape.
The resulting product has a high degree of detail and strength and an excellent surface finish due to its internal support structure (the mold itself). Products produced by rotational Molding include automotive parts, toys, medical devices, plumbing fixtures, sporting equipment, and construction equipment components.

Conclusion
Plastic Molding is one of the most application-dependent processes in the additive manufacturing field. It varies from part to part and from different companies, so it is important for anyone looking into this method to do their research. The information provided above does not constitute a complete list of all relevant factors but should serve as a broad overview to whet your appetite and help you get started.