Manufacturing products in large quantities is an industry where the largest savings can be found by companies that can mass produce their goods. Products like toys, gifts, advertising, and more are often very profitable for the ones who can manufacture them the fastest and the cheapest. As much as 20% of all goods manufactured worldwide depend on computer numerical control (CNC) machining processes. This percentage only increases because products that require precision in multiple parts are much easier to manufacture using these advanced processes. One important element of all CNC machining processes is application-specific software allowing any manufacturer to create parts with high precision and accuracy. The most common CNC machining processes include extrusion, milling (contour), profiling, drilling, grinding, laser cutting, and waterjet.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a metalworking process that uses a die to force a raw material (usually metal) through a shaped hole. It is one of the most basic ways to form metal parts and can be used to create pipes, tubes, and even solid bars.
In the extrusion process, molten metal is forced through a die or tool to create a finished product. The shape of the die determines the extruded profile of the material. Extrusion dies are usually made from hardened steel or carbide. This die type can be custom-made for each application or purchased off-the-shelf from companies.

Milling
Milling involves removing material from the surface of a workpiece with a rotating cutting tool held in place by a milling machine. Milling can be used for drilling holes but is also suitable for shaping large material areas. The process produces no chips, so no coolants or lubricants are needed. However, it does generate heat which can damage sensitive materials such as rubber and plastic.

Profiling
Profiling is the most common process in CNC machining. In this process, a cutter with a round or square profile is used to remove material from a workpiece. The precision of this process makes it possible for different types of parts to be made using the same tooling.
A CNC profiler can be used for many different types of parts and materials. It can also be used for complex shapes and contours that are difficult to produce using other machining methods.
CNC profiling can be done at high speeds but with very little removal of material, and as such, it is often used when producing prototypes or low-volume production runs. Because the accuracy of CNC profiling is so high, there is no need to go through any secondary processes such as grinding or polishing after machining has been completed.

Drilling
Drilling is the process of making holes in a material. Drilling is usually performed in conjunction with other machining processes such as turning, milling, broaching, and grinding.
Drilling can be done manually by using a drill press or manually operated machine tools, or it can be done by CNC machining with a CNC drilling machine.
In manual drilling, the object to be drilled is clamped in place and its position fixed concerning the axis of rotation (usually vertical) of the drill bit. The drill bit is then lowered into the workpiece at the starting point for the hole. The drill bit is then rotated at high speed and fed into the workpiece until it exits on the opposite side of where it started.

Grinding
Grinding is a machining process where a grinding wheel removes material from a surface. It is often used to prepare a surface for welding or finishing due to its relatively low cost and high production speed. Grinding can also be used with other processes, such as turning, milling, broaching, drilling and sawing.
Grinding can be done on various materials, including metal alloys (e.g., steel), plastics, and ceramics. Different tools are used for grinding depending on the ground material and the desired surface finish. These include:
Abrasive wheels: these are made from cemented carbide or steel; they have an abrasive coating that wears away as they come into contact with the workpiece
Granite wheels: these are made from rock-hard stones that are pressed together under great pressure; they are used for very hard materials like diamonds
Aluminum oxide disks: these are made from aluminum oxide powder mixed with water; they wear away quickly but produce a good finish.

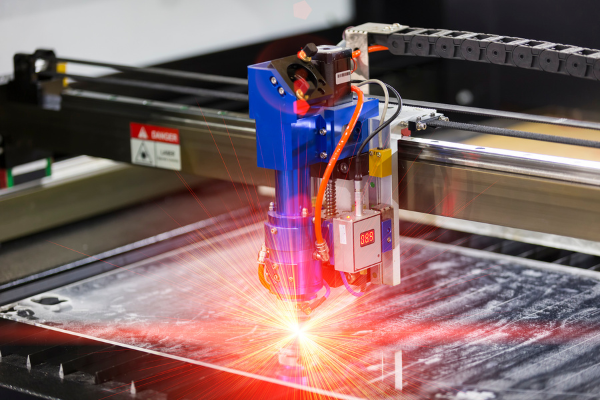
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is when a high-powered laser beam melts and cuts through materials. Laser cutting shapes metal, wood, plastic, and other materials. The laser beam is highly focused and directed by computer-aided design (CAD) software or manually to cut materials precisely.
Laser cutting can be done in two ways: direct process or indirect process. In the direct process, the material is placed on the table of the laser cutting machine. The material moves with the help of a table that slides along rails. In the indirect process, the material moves while the table remains stationary.
Laser cutting can make complex shapes impossible with traditional methods of cutting metals such as sawing or milling.

Waterjet
Waterjet cutting is a manufacturing process for cutting materials similar to laser cutting. In waterjet cutting, a high-pressure jet of water or other fluid such as air or oil is used to cut materials by erosion. The process uses a supply of high-pressure water (or other fluid) that is sent through a small nozzle under pressure to cut through the material. Waterjets have been used in industry since the 1950s and are available in sizes ranging from small handpieces to hydraulically operated machines capable of producing parts up to 30 feet (9 m) long.
Waterjet cutting is an excellent alternative to conventional machining processes such as milling, turning, drilling, and sawing when speed, accuracy, and surface finish are important factors. Waterjets can cut virtually any material, including plastics, composites, rubber, and metal.
Advantages over conventional machining processes include:
High-quality finish with no heat-affected zone (HAZ).
There is virtually no vibration or recoil because there are no moving parts in contact with the workpiece other than the high-pressure jet, which minimizes chatter marks on delicate materials.
Ability to cut any material, which means it can be used on thin sheet metals.

Conclusion
Ultimately, the machining process you choose will depend on your project, goals, and various other factors. Therefore, we can’t make a broad statement about which type of CNC machine is best—there are just too many variables involved in each scenario. However, if you know what to look for, you should be able to make the best choice possible for your particular situation.